1、source 命令
1 | source filename |
在当前 bash 环境下读取并执行 filename 中的命令。
2、环境变量分为 永久环境变量 和 临时环境变量
永久环境变量:修改配置文件,/etc/profile, /etc/.bashrc, ~/.profile, ~/.bashrc 等,
临时环境变量:使用 export 命令声明即可,变量在关闭shell时失效。
3、/etc/profile, /etc/.bashrc, ~/.profile, ~/.bashrc
这四个文件都是存储环境配置的,其中 /etc/profile, /etc/.bashrc 对全部用户有效,~/.profile, ~/.bashrc 对当前用户有效,执行的顺序为:
/etc/profile先执行,设置全部用户的环境配置。它会调用/etc/.bashrc和/etc/profile.d中的*.sh文件,其内容如下:
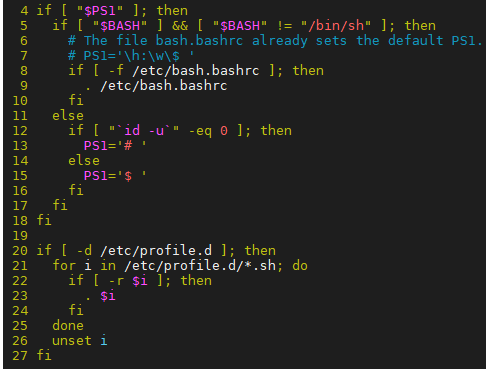
由代码可见,第 9 行,-f 判断文件存在则执行 /etc/bash.bashrc 文件(和/etc/.bashrc一样,不同的发行版命名略微有差异),接着,-d 判断 /etc/profile.d 目录存在,则在第21--24 行使用 for 循环依次执行每一个 *.sh 文件。(其中第 23 行 . $i 和 source $i 的作用是一样的)
~/.profile在每个用户登录时调用,它会调用~/.bashrc文件,其内容如下:
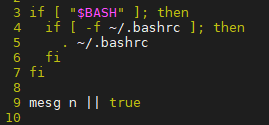
也就是说,我开机以 xxx 的身份登录系统时,先是会运行 /etc/profile 文件,然后根据我的身份运行对应的 ~/.profile 文件(只在登录时运行一次,更改后需要重启或者source **生效),它调用 ~/.bashrc 文件(每打开一个新的 shell 终端都会运行一次,更改后自动生效)。
4、有了 profile 为什么需要 bashrc 文件呢?
profile文件只有在登录的时候执行一次,bashrc是每打开一个shell都会执行一次,时效性很好。也就是所谓的 login shell 和 non-login shell 的区别。
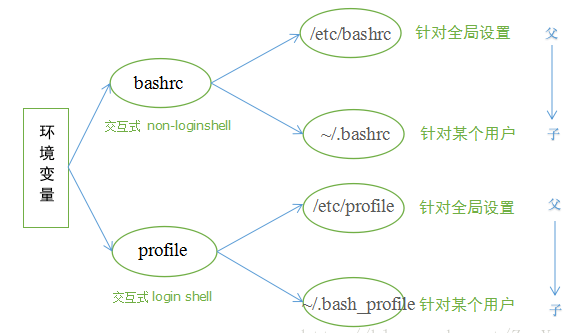
login shell : 取得bash 时需要完整的登入流程,就称为login shell。举例来说,同tty1~tty6登入时, 需要输入用户名和密码,此时取得的bash就称为login shell。
non-login shell: 取得bash 界面的方法不需要重复登入的动作。举例来说,以图形界面登录linux系统时,按 ctrl + alt + T 组合键打开的 shell 终端,就是 non-login shell。
