一、Money robbing
1、optimal substructure and DP equation
对于第 i 家,有两种选择,抢或者不抢。如果抢第 i 家,那么最大收益为:value[i] + 抢前 i-2 家的最优收益; 如果第 i 家不抢,那么最大收益为:抢前 i-1 家的最优收益。
状态转移方程可写为:
$$
dp[i] = max( dp[i-1], dp[i-2]+value[i] )
$$
2、 pseudo-code
1 | class Solution { |
3、 correctness of algorithm
如果暴力求解的话,每一家都有可能抢或者不抢,枚举每一种可能性,那么总的时间复杂度为 $O(2^n)$ ,且最后算出来的最优解一定是正确的。现在,我们采用动态规划思想中的 memory 数组,记录前 i-1 家的最优值,当计算第 i 家最优值时,其依赖的 OPT[i-1] 和 OPT[i-2] 已经求出,可直接计算当前最优值,故算法是正确的。
4、 complexity of algorithm
代码中的 dp 数组,每个元素只计算了一遍,故算法的时间复杂度为 $ O(n) $。
注:
当房屋变成一个环的时候,也就是相当于在原有问题上添加了一个限制条件:第1家和第n家不能同时抢。那么,分别计算抢第二家到最后一家与抢第一家到倒数第二家的最大值,取两个值中更大的那个就是结果。
1 | class Solution { |
二、Node selection
1、optimal substructure and DP equation
对于当前根节点,有两种可能性,选取或者不选取。如果选取了当前的根节点,那么其孩子节点就不能选取,即最优值变为:root->value + 4个孙子的最优值之和; 如果当前根节点没有选取,最优值变为:两个孩子节点最优值之和。
给定任意一个根,假设我们能够得到当前根选取与不选取的最优值,结果保存在一个长度为2的数组里,array[0]代表根节点不选取,array[1]代表根节点选取,那么最优解为:
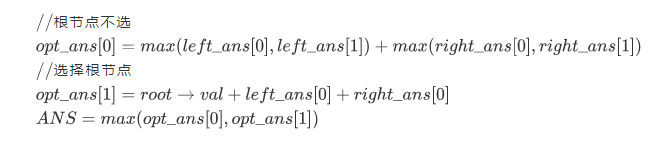
2、 pseudo-code
1 | class Solution { |
3、correctness of algorithm
当前节点的最优值,依赖于其儿子节点的最优值(当前节点没选,最优值等于选其左孩子节点最优值+选其右孩子节点最优值)或其孙子节点的最优值(选取了当前节点,最优值等于根节点值+其左孩子不选左根的最优值+右孩子不选右根的最优值),由此可知算法的正确性。
4、complexity of algorithm
整个算法相当于一个深度优先搜索(DFS),树中的每个节点都会遍历一次,故算法的时间复杂度为$O(n)$。
三、Decoding
1、optimal substructure and DP equation
dp[i]表示从字符0~i的字符串包含最多的编码种数。不考虑特殊情况,该题的递推式是$dp[i]=dp[i-1]+dp[i-2]$,因为一个数字可以表示一个编码,两个数字也有可能表示一个编码,所以dp[i]应该等于0~i-1的字符串包含的最多编码种数加上0~i-2的字符串包含的最多编码种数。但是考虑到一共只有26种基础编码加上特殊情况0,所以递推式可以表示为:
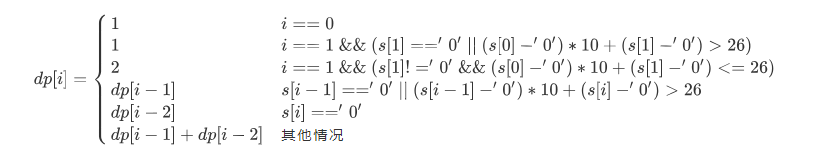
2、 pseudo-code
1 | class Solution { |
3、correctness of algorithm
首先该问题包含最优子结构的性质,求0~n的字符串包含最多的编码种数包含了求0~n-1的字符串包含最多的编码种数或0~n-2的字符串包含最多的编码种数。其次该问题包含重叠子性质,大量子问题会重复计算,如求dp[5]需要计算dp[4]或dp[3],求dp[4]需要求dp[3]或dp[2],因此dp[3]被重复计算。综上该问题可以用动态规划方法解且求解方程正确。
4、complexity of algorithm
整个求解过程只遍历了一遍字符串,故算法时间复杂度为$O(n)$。
六、OJ第一题
LIS,DP入门第一题,没啥好说的,只要想清楚为啥每次将新来的数据往 ans 数组里插入,最后出来的就一定是最长的就可以了。
1 |
|
七、OJ第二题
入门级题目外加了求 K 个最优值的条件,昨晚1点多打开题目,感觉随便码一码随便A掉,于是上床 睡觉,躺床上拍脑袋理论AC。仔细一想,K个最优值的状态转移,有点问题啊,带着疑问入睡不咋舒坦,大半夜将题目发到315群,杨老师帅气得给出了解决方案,顺带嘲笑了一波数据;炸老师看了数据量也嘲讽了一波;早上起来交了一发,发现 0 ms的时候,也疯狂鄙视一波,数据真的弱得不行。
想起来当年 ycb 的誓言:

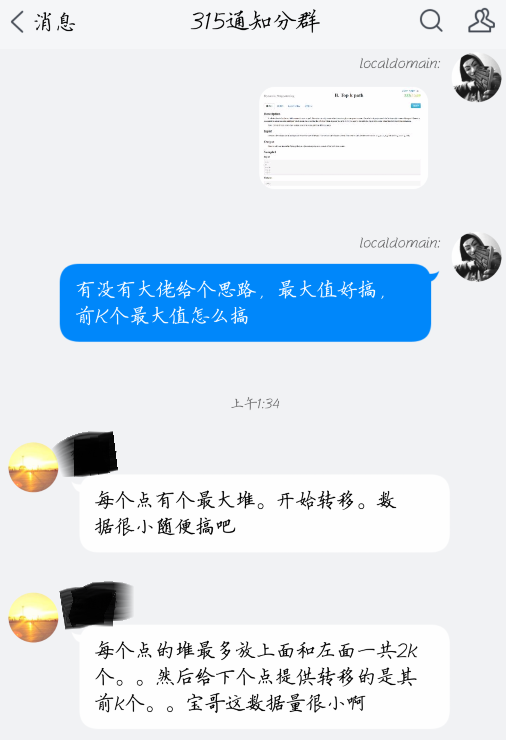
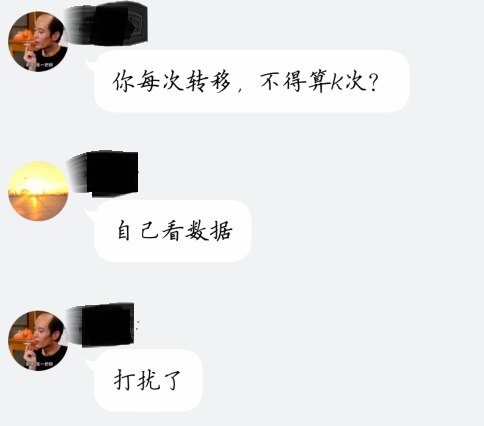
1 |
|
